In the previous article, the author covered the topic of prostate cancer, risk factors for the disease, symptoms that men may experience, and information on the cancer’s four phases.
In this segment, the importance of annual prostate cancer screenings for men, available treatment for men who have been diagnosed with this form of cancer, and methods to prevent it will be addressed.
Screening for Prostate Cancer
Cancer screening entails finding the disease before it manifests any symptoms. Finding cancers that may be at a high risk of spreading if not treated and catching them early before they spread are the two main objectives of prostate cancer screening.
There are two different kinds of screening test such as;
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Test
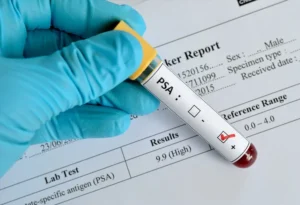
This test will check the blood’s PSA concentration. The prostate produces a chemical called PSA. Men with prostate cancer may have elevated blood PSA concentrations. Other prostate-related conditions might also cause the PSA level to rise.
The risk of a prostate condition is typically increased by a blood PSA result that is higher than normal. On the other hand, PSA levels can be impacted by things like certain medical procedures, medications, an enlarged prostate, or a prostate infection.
Digital Rectal Examination (DRE)
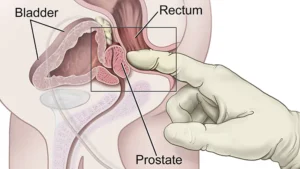
The DRE is arguably the most frequent test used in urological practise. The prostate gland must be palpated for induration or abnormal masses by inserting a finger into the rectum.
It is strongly advised that all men have their annual prostate cancer screenings. The screenings ought to begin at;
- if the average risk of prostate cancer development is at age 50,
- if there is a high chance of acquiring prostate cancer by age 45,
- if the risk of acquiring prostate cancer is very high by age 40.
Treatment Options for Prostate Cancer
These are the main treatments of prostate cancer. The ideal strategy mostly combines two or more of these therapeutic approaches. The treatment’s goal is to reduce symptoms.
Surgery
A radical prostatectomy involves removing the entire prostate gland, along with the urethra that passes through it and any seminal vesicles that are connected. For men with clinically localised prostate cancer and a 10-year or longer life expectancy, radical prostatectomy is a suitable course of treatment.
Hormonal Therapy
Androgen deprivation therapy is the first-line hormonal treatment for metastatic, advanced prostate cancer (ADT). It can both lessen symptoms and decrease the progression of prostate cancer to prolong life, even if it is not a curative treatment in such situation.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy can reduce prostate cancer symptoms and lengthen life in patients with metastatic prostate cancer. It is typically applied to prostate cancer that is resistant to castration.
Radiation therapy
Uses high-energy rays (similar to x-rays) to eliminate the cancer.
- External radiation therapy: a machine outside the body which focuses on radiation towards the cancer cells.
- Internal radiation therapy: radioactive seeds or pellets that are surgically inserted into or close to the malignancy to kill the cancer cells
Prevention of Prostate Cancer

These are the necessary steps that every men need to take in order to lower the risk of diagnosing prostate cancer;
- Eat more fruit and vegetables and lessen the intake of fat calories.
- Do regular exercise and maintain weight.
- Stop smoking and drink less alcohol.
- Increase the intake of Vitamin D supplements.
Do not hesitate to seek advice from your trusted doctors if you notice any issues or want to learn more about prostate cancer.
Stay safe and healthy!
Source: [1,2]
Follow us on Instagram, Facebook or Telegram for more updates and breaking news.